Urbanization, natural increase and centripetal population movements

Source: https://www.slideshare.net/stevenheath148/urbanization-centripetal-and-centrifugal-movements
Source: IB Geography: Course Book 2nd edition: Oxford IB Diploma Program

Source: http://slideplayer.com/slide/7352296/

Source: http://slideplayer.com/slide/7278656/


Source: https://cleanupjamaicaqueens.wordpress.com/2014/02/28/gentrification-is-a-good-thing-ghettoization-is-not/

Source: https://therealdeal.com/2014/01/19/starbucks-portends-gentrification-in-inwood-brokers-say/








Nagle, Garrett, and Briony Cooke. Geography Course Companion. 2nd ed., Oxford University Press, 2017, pp. 352-356.

Source: http://slideplayer.com/slide/7352296/
Source: http://slideplayer.com/slide/7278656/
Centripetal population movements
Rural-urban migration

Source: https://www.slideshare.net/stevenheath148/urbanization-centripetal-and-centrifugal-movements

Source: https://www.slideshare.net/stevenheath148/urbanization-centripetal-and-centrifugal-movements
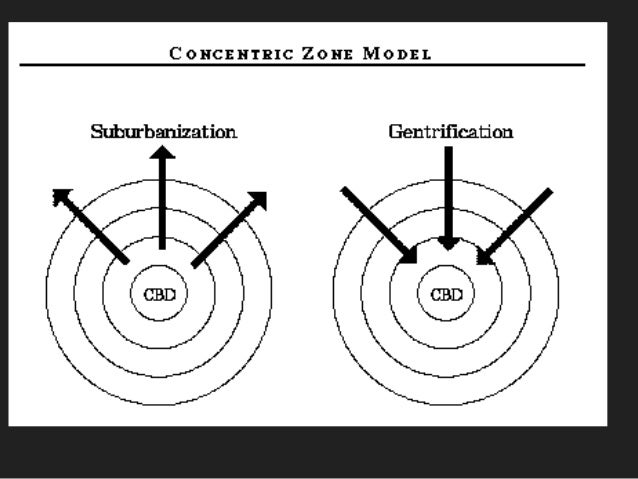
Gentrification and reurbanization

Source: https://cleanupjamaicaqueens.wordpress.com/2014/02/28/gentrification-is-a-good-thing-ghettoization-is-not/

Source: https://therealdeal.com/2014/01/19/starbucks-portends-gentrification-in-inwood-brokers-say/


Centrifugal population movements
Suburbanization



Source: https://www.slideshare.net/stevenheath148/urbanization-centripetal-and-centrifugal-movements
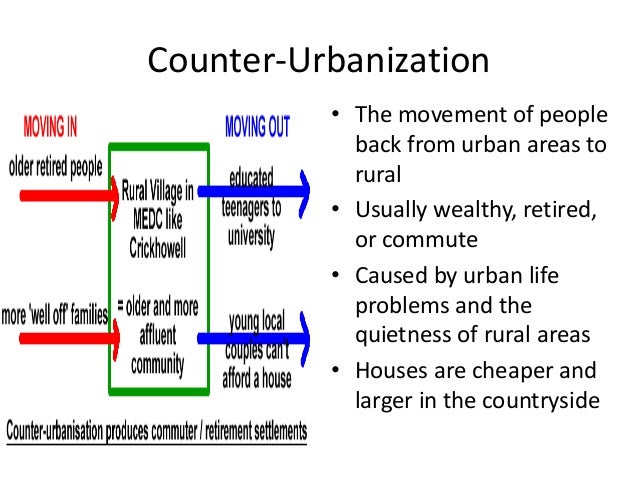
Counter-urbanization



Source: https://www.slideshare.net/stevenheath148/urbanization-centripetal-and-centrifugal-movements
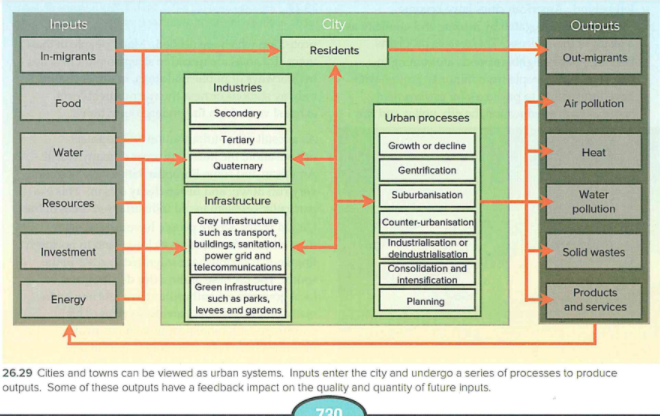
Urban systems growth
Source: Codrington, S. (2017). Planet geography. 2nd edition. Sydney: Solid Star Press.
Case study of infrastructure growth over time in one city - Shanghai, China
More about infrastructure development in Shanghai at at:
Nagle, Garrett, and Briony Cooke. Geography Course Companion. 2nd ed., Oxford University Press, 2017, pp. 352-356.
The causes of urban deindustrialization and its economic, social and demographic consequences
Source: https://oxfamblogs.org/fp2p/why-premature-deindustrialization-is-really-bad-news-for-development/
Deindustrialization is the long-term, absolute decline in employment in the manufacturing sectors of an economy. It refers to a loss of jobs rather than a decline in productivity. The decline of certain industries or areas is due to a number of factors, including:
- the exhaustion of resources
- the increasing costs of raw materials
- automation and new technology
- the introduction of a rival product
- fall in demand
- overseas competition from NICs
- rationalization
- a rise in costs
- the removal of a subsidy
- lack of capital
Source: IB Geography: Course Book 2nd edition: Oxford IB Diploma Program
Synthesis (Sy), Evaluation (Ev) and Skills (Sk) opportunities
Use the content of this post to plan and answer the following question: ‘Contrasts in the scale of changes and challenges facing different urban areas’. 10 marks.
Use markscheme on page 56 from the new syllabus guide (AO3).







No comments:
Post a Comment